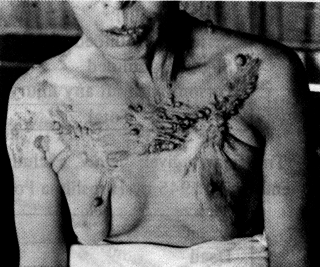
| The effect of radiation had a synergistic action with the burns due to
thermal radiation and fire and the injuries due to the blast and generally aggravated the
condition of the diseases of those exposed. Delaved effects of radiation are divided into acute sickness and long-term illness according to the time of their development.Acute sickness is a symptom that devel-oped in the period from the time of the explosion to the end of December the same year, and rnost of the people are said to have recovered from the symptoms 5 months after the explosion. They are: digestive symptoms (nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea); nerve symptoms (headache, delirious utterance, and insomnia); adynamic symptoms |
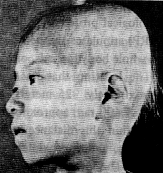 |
| (epilation, weakness, and malaise); bleeding symptoms (hematemesis, bloody discharge from the bowels, hematuria, nosebleed, gingival bleeding, genital bleeding, and subcuta-neous bleeding); inflammation symptoms (fever, pharyngalgia, stomatitis, and dermatitis); blood symptoms (leukocytopenia and erythrocytopenia); genital organ symptoms (aspermia and menstrual abnormalities). | A girl in hair epliation stage. (2 km from the hypocenter photographed by Shunkichi Kikuchi.) |